Introduction
Neural networks are an example of composable systems, so it’s no surprise that they can be modeled in category theory, which is the ultimate science of composition. Moreover, the categorical ideas behind neural networks can be immediately implemented and tested in a programming language. In this post I will present the Haskell implementation of parametric lenses, generalize them to pre-lenses and introduce their profunctor representation. Using the profunctor representation I will build a working multi-layer perceptron.
In the second part of this post I will introduce the bicategory 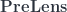 of pre-lenses and the bicategory of triple Tambara profunctors and show how they related to pre-lenses.
of pre-lenses and the bicategory of triple Tambara profunctors and show how they related to pre-lenses.
Complete Haskell implementation is available on gitHub, where you can also find the PDF version of this post, complete with the categorical picture.
Haskell Implementation
Every component of a neural network can be thought of as a system that transform input to output, and whose action depends on some parameters. In the language of neural networsks, this is called the forward pass. It takes a bunch of parameters p, combines it with the input s, and produces the output a. It can be described by a Haskell function:
fwd :: (p, s) -> a
But the real power of neural networks is in their ability to learn from mistakes. If we don’t like the output of the network, we can nudge it towards a better solution. If we want to nudge the output by some da, what change dp to the parameters should we make? The backward pass partitions the blame for the perceived error in direct proportion to the impact each parameter had on the result.
Because neural networks are composed of layers of neurons, each with their own sets or parameters, we might also ask the question: What change ds to this layer’s inputs (which are the outputs of the previous layer) should we make to improve the result? We could then back-propagate this information to the previous layer and let it adjust its own parameters. The backward pass can be described by another Haskell function:
bwd :: (p, s, da) -> (dp, ds)
The combination of these two functions forms a parametric lens:
data PLens a da p dp s ds =
PLens { fwd :: (p, s) -> a
, bwd :: (p, s, da) -> (dp, ds) }
In this representation it’s not immediately obvious how to compose parametric lenses, so I’m going to present a variety of other representations that may be more convenient in some applications.
Existential Parametric Lens
Notice that the backward pass re-uses the arguments (p, s) of the forward pass. Although some information from the forward pass is needed for the backward pass, it’s not always clear that all of it is required. It makes more sense for the forward pass to produce some kind of a care package to be delivered to the backward pass. In the simplest case, this package would just be the pair (p, s). But from the perspective of the user of the lens, the exact type of this package is an internal implementation detail, so we might as well hide it as an existential type m. We thus arrive at a more symmetric representation:
data ExLens a da p dp s ds =
forall m . ExLens ((p, s) -> (m, a))
((m, da) -> (dp, ds))
The type m is often called the residue of the lens.
These existential lenses can be composed in series. The result of the composition is parameterized by the product (a tuple) of the original parameters. We’ll see it more clearly in the next section.
But since the product of types is associative only up to isomorphism, the composition of parametric lenses is associative only up to isomorphism.
There is also an identity lens:
identityLens :: ExLens a da () () a da
identityLens = ExLens id id
but, again, the categorical identity laws are satisfied only up to isomorphism. This is why parametric lenses cannot be interpreted as hom-sets in a traditional category. Instead they are part of a bicategory that arises from the 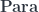 construction.
construction.
Pre-Lenses
Notice that there is still an asymmetry in the treatment of the parameters and the residues. The parameters are accumulated (tupled) during composition, while the residues are traced over (categorically, an existential type is described by a coend, which is a generalized trace). There is no reason why we shouldn’t accumulate the residues during composition and postpone the taking of the trace untill the very end.
We thus arrive at a fully symmetrical definition of a pre-lens:
data PreLens a da m dm p dp s ds =
PreLens ((p, s) -> (m, a))
((dm, da) -> (dp, ds))
We now have two separate types: m describing the residue, and dm describing the change of the residue.

If all we need at the end is to trace over the residues, we’ll identify the two types.
Notice that the role of parameters and residues is reversed between the forward and the backward pass. The forward pass, given the parameters and the input, produces the output plus the residue. The backward pass answers the question: How should we nudge the parameters and the inputs (dp, ds) if we want the residues and the outputs to change by (dm, da). In neural networks this will be calculated using gradient descent.
The composition of pre-lenses accumulates both the parameters and the residues into tuples:
preCompose ::
PreLens a' da' m dm p dp s ds ->
PreLens a da n dn q dq a' da' ->
PreLens a da (m, n) (dm, dn) (q, p) (dq, dp) s ds
preCompose (PreLens f1 g1) (PreLens f2 g2) = PreLens f3 g3
where
f3 = unAssoc . second f2 . assoc . first sym .
unAssoc . second f1 . assoc
g3 = unAssoc . second g1 . assoc . first sym .
unAssoc . second g2 . assoc
We use associators and symmetrizers to rearrange various tuples. Notice the separation of forward and backward passes. In particular, the backward pass of the composite lens depends only on backward passes of the composed lenses.
There is also an identity pre-lens:
idPreLens :: PreLens a da () () () () a da
idPreLens = PreLens id id
Pre-lenses thus form a bicategory that combines the 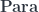 and the
and the 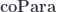 constructions in one.
constructions in one.
There is also a monoidal structure in this category induced by parallel composition. In parallel composition we tuple the respective inputs and outputs, as well as the parameters and residues, both in the forward and the backward passes.
The existential lens can be obtained from the pre-lens at any time by tracing over the residues:
data ExLens a da p dp s ds =
forall m. ExLens (PreLens a da m m p dp s ds)
Notice however that the tracing can be performed after we are done with all the (serial and parallel) compositions. In particular, we could dedicate one pipeline to perform forward passes, gathering both parameters and residues, and then send this data over to another pipeline that performs backward passes. The data is produced and consumed in the LIFO order.
Pre-Neuron
As an example, let’s implement the basic building block of neural networks, the neuron. In what follows, we’ll use the following type synonyms:
type D = Double
type V = [D]
A neuron can be decomposed into three mini-layers. The first layer is the linear transformation, which calculates the scalar product of the input vector and the vector of parameters:
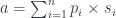
It also produces the residue which, in this case, consists of the tuple (V, V) of inputs and parameters:
fw :: (V, V) -> ((V, V), D)
fw (p, s) = ((s, p), sumN n $ zipWith (*) p s)
The backward pass has the general signature:
bw :: ((dm, da) -> (dp, ds))
Because we’re eventually going to trace over the residues, we’ll use the same type for dm as for m. And because we are going to do arithmetic over the parameters, we reuse the type of p for the delta dp. Thus the signature of the backward pass is:
bw :: ((V, V), D) -> (V, V)
In the backward pass we’ll encode the gradient descent. The steepest gradient direction and slope is given by the partial derivatives:
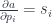

We multiply them by the desired change in the output da:
dp = fmap (da *) s
ds = fmap (da *) p
Here’s the resulting lens:
linearL :: Int -> PreLens D D (V, V) (V, V) V V V V
linearL n = PreLens fw bw
where
fw :: (V, V) -> ((V, V), D)
fw (p, s) = ((s, p), sumN n $ zipWith (*) p s)
bw :: ((V, V), D) -> (V, V)
bw ((s, p), da) = (fmap (da *) s
,fmap (da *) p)
The linear transformation is followed by a bias, which uses a single number as the parameter, and generates no residue:
biasL :: PreLens D D () () D D D D
biasL = PreLens fw bw
where
fw :: (D, D) -> ((), D)
fw (p, s) = ((), p + s)
-- da/dp = 1, da/ds = 1
bw :: ((), D) -> (D, D)
bw (_, da) = (da, da)
Finally, we implement the non-linear activation layer using the tanh function:
activL :: PreLens D D D D () () D D
activL = PreLens fw bw
where
fw (_, s) = (s, tanh s)
-- da/ds = 1 + (tanh s)^2
bw (s, da)= ((), da * (1 - (tanh s)^2))
A neuron with  inputs is a composition of the three components, modulo some monoidal rearrangements:
inputs is a composition of the three components, modulo some monoidal rearrangements:
neuronL :: Int ->
PreLens D D ((V, V), D) ((V, V), D) Para Para V V
neuronL mIn = PreLens f' b'
where
PreLens f b =
preCompose (preCompose (linearL mIn) biasL) activL
f' :: (Para, V) -> (((V, V), D), D)
f' (Para bi wt, s) = let (((vv, ()), d), a) =
f (((), (bi, wt)), s)
in ((vv, d), a)
b' :: (((V, V), D), D) -> (Para, V)
b' ((vv, d), da) = let (((), (d', w')), ds) =
b (((vv, ()), d), da)
in (Para d' w', ds)
The parameters for the neuron can be conveniently packaged into one data structure:
data Para = Para { bias :: D
, weight :: V }
mkPara (b, v) = Para b v
unPara p = (bias p, weight p)
Using parallel composition, we can create whole layers of neurons, and then use sequential composition to model multi-layer neural networks. The loss function that compares the actual output with the expected output can also be implemented as a lens. We’ll perform this construction later using the profunctor representation.
Tambara Modules
As a rule, all optics that have an existential representation also have some kind of profunctor representation. The advantage of profunctor representations is that they are functions, and they compose using function composition.
Lenses, in particular, have a representation using a special category of profunctors called Tambara modules. A vanilla Tambara module is a profunctor p equipped with a family of transformations. It can be implemented as a Haskell class:
class Profunctor p => Tambara p where
alpha :: forall a da m. p a da -> p (m, a) (m, da)
The vanilla lens is then represented by the following profunctor-polymorphic function:
type Lens a da s ds = forall p. Tambara p => p a da -> p s ds
A similar representation can be constructed for pre-lenses. A pre-lens, however, has additional dependency on parameters and residues, so the analog of a Tambara module must also be parameterized by those. We need, therefore, a more complex type constructor t that takes six arguments:
t m dm p dp s ds
This is supposed to be a profunctor in three pairs of arguments, s ds, p dp, and dm m. Pro-functoriality in the first two pairs is implemented as two functions, diampS and dimapP. The inverted order in dm m means that t is covariant in m and contravariant in dm, as seen in the unusual type signature of dimapM:
dimapM :: (m -> m') -> (dm' -> dm) ->
t m dm p dp s ds -> t m' dm' p dp s ds
To generalize Tambara modules we first observe that the pre-lens now has two independent residues, m and dm, and the two should transform separately. Also, the composition of pre-lenses accumulates (through tupling) both the residues and the parameters, so it makes sense to use the additional type arguments to TriProFunctor as accumulators. Thus the generalized Tambara module has two methods, one for accumulating residues, and one for accumulating parameters:
class TriProFunctor t => Trimbara t where
alpha :: t m dm p dp s ds ->
t (m1, m) (dm1, dm) p dp (m1, s) (dm1, ds)
beta :: t m dm p dp (p1, s) (dp1, ds) ->
t m dm (p, p1) (dp, dp1) s ds
These generalized Tambara modules satisfy some coherency conditions.
One can also define natural transformations that are compatible with the new structures, so that Trimbara modules form a category.
The question arises: can this definition be satisfied by an actual non-trivial TriProFunctor? Fortunately, it turns out that a pre-lens itself is an example of a Trimbara module. Here’s the implementation of alpha for a PreLens:
alpha (PreLens fw bw) = PreLens fw' bw'
where
fw' (p, (n, s)) = let (m, a) = fw (p, s)
in ((n, m), a)
bw' ((dn, dm), da) = let (dp, ds) = bw (dm, da)
in (dp, (dn, ds))
and this is beta:
beta (PreLens fw bw) = PreLens fw' bw'
where
fw' ((p, r), s) = let (m, a) = fw (p, (r, s))
in (m, a)
bw' (dm, da) = let (dp, (dr, ds)) = bw (dm, da)
in ((dp, dr), ds)
This result will become important in the next section.
TriLens
Since Trimbara modules form a category, we can define a polymorphic function type (a categorical end) over Trimbara modules . This gives us the (tri-)profunctor representation for a pre-lens:
type TriLens a da m dm p dp s ds =
forall t. Trimbara t => forall p1 dp1 m1 dm1.
t m1 dm1 p1 dp1 a da ->
t (m, m1) (dm, dm1) (p1, p) (dp1, dp) s ds
Indeed, given a pre-lens we can construct the requisite mapping of Trimbara modules simply by lifting the two functions (the forward and the backward pass) and sandwiching them between the two Tambara structure maps:
toTamb :: PreLens a da m dm p dp s ds ->
TriLens a da m dm p dp s ds
toTamb (PreLens fw bw) = beta . dimapS fw bw . alpha
Conversely, given a mapping between Trimbara modules, we can construct a pre-lens by applying it to the identity pre-lens (modulo some rearrangement of tuples using the monoidal right/left unit laws):
fromTamb :: TriLens a da m dm p dp s ds ->
PreLens a da m dm p dp s ds
fromTamb f = dimapM runit unRunit $
dimapP unLunit lunit $
f idPreLens
The main advantage of the profunctor representation is that we can now compose two lenses using simple function composition; again, modulo some associators:
triCompose ::
TriLens b db m dm p dp s ds ->
TriLens a da n dn q dq b db ->
TriLens a da (m, n) (dm, dn) (q, p) (dq, dp) s ds
triCompose f g = dimapP unAssoc assoc .
dimapM unAssoc assoc .
f . g
Parallel composition of TriLenses is also relatively straightforward, although it involves a lot of bookkeeping (see the gitHub implementation).
Training a Neural Network
As a proof of concept, I have implemented and trained a simple 3-layer perceptron.
The starting point is the conversion of the individual components of the neuron from their pre-lens representation to the profunctor representation using toTamb. For instance:
linearT :: Int -> TriLens D D (V, V) (V, V) V V V V
linearT n = toTamb (linearL n)
We get a profunctor representation of a neuron by composing its three components:
neuronT :: Int ->
TriLens D D ((V, V), D) ((V, V), D) Para Para V V
neuronT mIn =
dimapP (second (unLunit . unPara))
(second (mkPara . lunit)) .
triCompose (dimapM (first runit) (first unRunit) .
triCompose (linearT mIn) biasT) activT
With parallel composition of tri-lenses, we can build a layer of neurons of arbitrary width.
layer :: Int -> Int ->
TriLens V V [((V, V), D)] [((V, V), D)] [Para] [Para] V V
layer mIn nOut =
dimapP (second unRunit) (second runit) .
dimapM (first lunit) (first unLunit) .
triCompose (branch nOut) (vecLens nOut (neuronT mIn))
The result is again a tri-lens, and such tri-lenses can be composed in series to create a multi-layer perceptron.
makeMlp :: Int -> [Int] ->
TriLens V V -- output
[[((V, V), D)]] [[((V, V), D)]] -- residues
[[Para]] [[Para]] -- parameters
V V -- input
Here, the first integer specifies the number of inputs of each neuron in the first layer. The list [Int] specifies the number of neurons in consecutive layers (which is also the number of inputs of each neuron in the following layer).
The training of a neural network is usually done by feeding it a batch of inputs together with a batch of expected outputs. This can be simply done by arranging multiple perceptrons in parallel and accumulating the parameters for the whole batch.
batchN :: (VSpace dp) => Int ->
TriLens a da m dm p dp s ds ->
TriLens [a] [da] [m] [dm] p dp [s] [ds]
To make the accumulation possible, the parameters must form a vector space, hence the constraint VSpace dp.
The whole thing is then capped by a square-distance loss lens that is parameterized by the ground truth values:
lossL :: PreLens D D ([V], [V]) ([V], [V]) [V] [V] [V] [V]
lossL = PreLens fw bw
where
fw (gTruth, s) =
((gTruth, s), sqDist (concat s) (concat gTruth))
bw ((gTruth, s), da) = (fmap (fmap negate) delta', delta')
where
delta' = fmap (fmap (da *)) (zipWith minus s gTruth)
In the next post I will present the categorical version of this construction.
:

is an object of
.

.
is not strict, the parametric composition and identity laws are not strict either. They are satisfied up to associators and unitors of
. A category with lax composition and identity laws is called a bicategory. The 2-cells in a parametric bicategory are called reparameterizations.
is a category in which we define an action of a monoidal category
:
and
. The first constructs parametric morphisms from
to
as
, and the second as
.
construction can be extended to optics, where we’re dealing with pairs of objects from the underlying category (or categories, in the case of mixed optics). The parameterized optic is defined as the following coend:
are objects of some monoidal category
, and the parameters
come from another monoidal category
.
in
to the pair of objects
also in
, parameterized by a pair
in
and a pair
from
.
for the category
, and bold letters for pairs of objects and (twisted) pairs of morphisms. For instance,
is a member of the hom-set
represented by a pair
.
to denote the monoidal action of
on
:
.
bicategory. The composition is a mapping:
and the second by
:
, as long as the two monoidal actions commute, that is, if we have:
,
, and
.
and
. Associativity and identity laws are satisfied modulo the associators and the unitors.
is monoidal, the
bicategory is also monoidal, with the obvious point-wise parallel composition of pre-optics.
to
must give the same result.
.
to be the trivial one-object monoidal category, we get a version of (double-) Tambara modules. If we then take the coend,
, we get regular Tambara modules.
, we can define a mapping
from the triple:
by
and rearranging the actions using their commutativity.
, we map:
can be expressed using triple Tambara modules. An optic:
and get an arbitrary pre-optic.




